Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland doesn’t create and release enough thyroid hormone into the bloodstream. It is found more common nowadays.
Thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland normally located in the lower front of the neck, secretes very important hormones -triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), Calcitonin – collectively called as Thyroid Hormones.
Its an important part of the endocrine system that play an important role in the regulation of our weight, energy levels, internal temperature, skin, hair, nail growth, and overall metabolism (the process in which your body transforms the food you eat into energy).
Presense of Thyroid Hormone
Thyroid hormone exists in mainly two forms – thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). T4 is the primary form of thyroid hormone circulating in the blood covering around 95%, while T3 accounts for around 5% of thyroid hormone circulating in the blood..
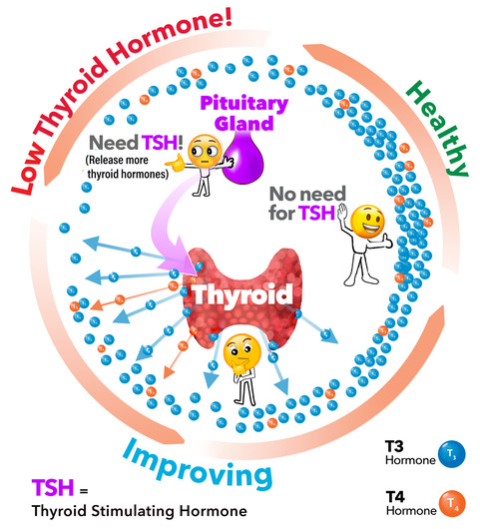
Production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland is controlled by the pituitary, another endocrine gland in the brain. The pituitary releases Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (abbreviated TSH) into the blood to stimulate the thyroid to make more thyroid hormone. The amount of TSH that the pituitary sends into the bloodstream depends on the amount of thyroid hormone in the body. T4 is converted to T3 by the removal of an iodine atom; this occurs mainly in the liver and in certain tissues where T3 acts, such as in the brain.
Test :
Measuring the TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) level in a blood sample is the best way to test thyroid function at initial level. TSH level change can serve as an early warning system before the actual level of thyroid hormones in the body becomes too high or too low. A high TSH level indicates that the thyroid gland is not making enough thyroid hormone (primary hypothyroidism).
In some thyroid diseases, the proportions of T3 and T4 in the blood change and can provide diagnostic information. A pattern of increased T3 vs T4 is characteristic of Graves’ disease. On the other hand, medications like steroids and amiodarone, and severe illness can decrease the amount of thyroid hormone the body converts from T4 to T3 (active form) resulting in a lower proportion of T3.
Normal ranges for thyroid tests may vary slightly among different laboratories, though I’m giving below a typical range for guidance.
TSH normal values are 0.5 to 5.0 mIU/L.
FT4 normal values are 0.7 to 1.9ng/dL.
Total T4 and Total T3 levels measure bound and free thyroid hormone in the blood. These levels are influenced by many factors that affect protein levels in the body, including medications, sex hormones, and liver disease.
Total T4 level in adults – 5.0 to 12.0μg/dL.
Total T3 level in adults : 80-220 ng/dL.
In some situation the levels of these hormones can be low without thyroid disease. Like any significant illness e:g. an infection, cancer, heart failure, liver disease, kidney disease, or recent recovery from an illness can cause transient changes in the TSH. Fasting or starvation can also cause a low TSH.
Interference – Few substances also can interfere in the results giving wrong conclusion. Biotin which is a common supplement for hair and nail growth does interferes with many thyroid function tests and can lead to inaccurate results. Endocrinologists recommend stopping biotin supplements for 3 days before having a blood test for thyroid function. Again who have exposure to mice, like laboratory researchers and veterinarians, may develop antibodies against mouse proteins in their blood. These antibodies cross react with reagents in multiple thyroid function tests and cause unpredictable results.
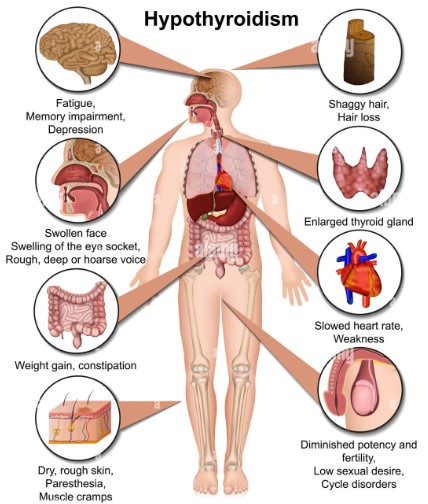
Sign and Symptoms of Hypothyroidism : Below are main Sign and symptoms of lower thyroid hormones or Hypothyroidism.
- Fatigue
- Weight Gain
- Muscles & Joints ache
- Slow movements & thoughts
- impaired concentration & memory
- loss of libido (sex drive)
- Low mood or depression
- sensitive to cold
- brittle hair & nails
- irregular periods
- numbness & tingling in hands
At the later stage it may also cause – anaemia, loss of hearing, slow heart rate, puffiness in eye & face, and low-pitched and hoarse voice etc.
Treatment of Hypothyroidism:
Allopathy/Modern Medicine- Levothyroxine is the standard of care in thyroid hormone replacement therapy and treatment of hypothyroidism. Levothyroxine (also called LT4) is equivalent to the T4 form of naturally occurring thyroid hormone.
Multiple medications and supplements decrease absorption of thyroid hormone and should be taken 3–4 hours apart, including calcium and iron supplements, proton pump inhibitors, soy, and multivitamins with minerals.
Liothyronine is replacement T3 (triiodothyronine) thyroid hormone. This medication has a short half-life and is taken twice per day or in combination with levothyroxine. Liothyronine alone is not used for treatment of hypothyroidism long term.
Homeopathy – Homeopathy works deep so its often more helpful in hard to cure diseases or royal diseases. But unlike modern medicine, it works on symptoms to choose the right medicine rather than the names of disease, different symptoms indicate to different causes for tha same disease. Thought to give a high level guideline, things medicines can be useful – Natrum Muriaticum, Silicia, Kali Carbonicum, Thyroidinum, Carcinocin, Calcaria Carbonicum, Iodium, Calcaria Iodum, Lycopodium Clavatum, Thuja Occidentalis, Sepia Officinalis etc. To ahve right medicine and in right way please contact a good doctor.
Food :
What to Eat : Its important to eat iodine rich iodine to help increase thyroid hormone levels.
Common example of high protein foods are – Eggs. Dairy products (for Vitamin D), meat & poulty, iodized salt, Omega-3 (found in fish/seafood and helps in immunity, lower risk of heart disease & decrease inflammation), Nuts being high in selenium, fresh fruit & vegetable specially blueberry & cherry, green peppers, seaweed (has fiber, calcium, and vitamins A, B, C, E, and K).
What to avoid Eating : People with hypothyroidism should limit their intake of cruciferous vegetables, such as broccoli and cabbage, to 5 ounces a day, as they can block the thyroid’s ability to absorb iodine, which is essential for normal thyroid function. Some researchers believe that too much soy may increase a person’s risk for hypothyroidism as it contains isoflavones. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli & cabbage, are full of fiber & other nutrients, but they may interfere with the production of thyroid hormone.
Hope you’ll find it useful and interesting. Please reach out to me for any help, using Contact page or or mail us at info@shikti.com or drsantkj@gmail.com.
Thanks, be Blessed
– Dr Sant



